Website security should be a top-of-mind concern for website owners. However, most of them do not think about web security until they encounter malware or ransomware attacks.
Website growth is increasing, and so are the cyber threats that proliferate the internet. But the lack of proactivity when it comes to web security is alarming. It causes businesses and enterprises to pay the high price of a non-secure website. Beyond the loss of money, loss of valuable data, and even online reputation can be one of the unfortunate results of an unsafe website.
With the intensity and ingenuity of cyberattacks increasing today, it is critical to invest time and money on website security, because website security at risk is a business at risk.
Your website’s Search Engine Optimization or SEO ranking is also compromised if your website is not safe. Google has about 200 ranking factors and more that determine Search Engine Results Page (SERP) rankings. Website security is one of the highest priorities.
If you get penalties for being an unsafe site, or worse, get taken down by search engines, you lose potential leads and customers for every day that your site is down.
So, SEO optimization of your website is never complete if your website is a web security risk. The question now is if your website is secure?
Table of Contents
- 1 How to Check if a Website is Secure
- 2 How Cybersecurity Affects SEO
- 2.1 1. Unsafe Sites Can Incur Penalties
- 2.2 2. Malicious Bots Stop Search Engine Crawlers
- 2.3 3. SEO Spam is Rampant
- 2.4 4. Integrate Security Audits in Your SEO Strategy
- 2.5 5. Fortify Your WordPress Security
- 2.6 6. Use the Best Malware-Scanning Tools
- 2.7 7. Get an SSL Certificate for Your Website
- 2.8 8. Local Network Security
- 3 Conclusion: Web Security Amps Your SEO
How to Check if a Website is Secure
The internet does not come with built-in security. That is why encryption is essential for every website to be secure. For individuals, you can easily check if a website’s connection is secure or not. Google support gives this simple guide:
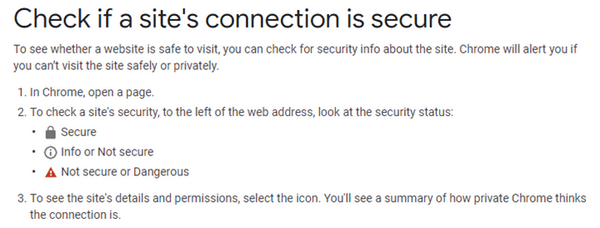
Secure: Information you send or get through the site is private. However, seeing this icon does not mean security is foolproof. You still need to be careful when you are sharing your private information. Always look at the address bar to ensure you are not being redirected to a malicious or dangerous site.
Info or Not Secure: The site is not using a private connection. It means that whatever information you share might be viewed and changed by someone. On some sites, you can visit a more secure version of the page by merely deleting http:// and changing it to https:// instead. If it does not work, contact the site owner and ask them to secure your data with HTTPS.
Not Secure or Dangerous: You might see a “Login not secure” or “Payment not secure” message. Do not enter any private or personal information on this page and get out of the site. But if it is a dangerous site, avoid it altogether, especially If you see a full-page red warning screen. It means the site has been flagged as unsafe by Safe Browsing, and using the site will put your private information at risk.
How Cybersecurity Affects SEO
Instead of merely concentrating on SEO strategies, from building links to marketing content, emphasize making the website a safe place for your readers. Cybersafety and SEO go together to push your website’s SEO rating effectively.
Be mindful of threats and cyberattacks that need to be resolved right away in case you encounter them.
1. Unsafe Sites Can Incur Penalties
Search engines are highly strict when identifying a 503 or 404 error on web sites, punishing the site immediately. They search websites diligently for malware, phishing attacks, and unauthorized apps that can damage and expose sensitive user data or make user experiences unpleasant. If Google detects attacks like DDoS or ransomware, it issues Manual Actions to the website.
When this happens, the rating of a website automatically gets affected. Users who search for your site will see a 404 page.
About 90% of unsafe sites are left unflagged. So the threat of cyberattacks and data breaches persists, leading to increased fines and a further decline in rankings. Therefore, search engines use an SSL certificate in their ranking algorithms as a vital factor.
Encrypt your website to ensure your website is secure. Your data, and your audience. If your website has no SSL certificate. Meaning confidential data is not encrypted and is vulnerable to breach.
2. Malicious Bots Stop Search Engine Crawlers
Search engines use bots to crawl through the web and collect indexing ranking parameters. However, bad bots such as scrapers, hacking bots, spammers, and click fraud can also crawl your site for content scraping and data breach. It puts your SEO rating at risk.
Scraping bots can plagiarize your content and republish it on other sites. When search engines discover the duplicate content first, they will mark your original content as the duplicate. Malicious bots make 29% of all site visits.
How do you know you are being attacked? Here are some signs:
- You cannot log in with your password.
- You experience recurring pop-ups or error messages.
- Suspicious JavaScript code.
Act promptly on Google alerts and updates. The moment Google warns you, or in your search results, you find a 404 or “Domain Not Available” message, presume it’s an attack and respond immediately.
Delete any suspicious-looking code in the source. Most hackers use JavaScript code to steal confidential website information.
3. SEO Spam is Rampant
Black hat hackers are the source of over 50% of malware attacks. They go after prominent websites by injecting links or JavaScript code to redirect visitors to malicious sites.
Spamdexing is also rampant. It is SEO spamming that pushes low-quality content on high-ranking sites, in turn, driving the ranking of these spam sites up. 73.9% of spam attacks contain SEO spam content.
It affects the SERP rankings of victim sites due to the spammy outbound links. It can damage site reputation and domain authority. Victim sites can also get blacklisted by search engines, that is why SEO and security teams need to work together to prevent such from happening.
4. Integrate Security Audits in Your SEO Strategy
Cybersecurity should and must be well-integrated into your SEO strategies. Because search engines penalize websites with poor cybersecurity. Regularly monitor your website’s security system. Address detect threats as soon as possible to preserve your SEO ranking.
You can even hire external web security services to support your IT team’s efforts in creating and maintaining website security. Patching vulnerabilities at the onset and keeping everything updated is an excellent way of keeping a robust preemptive cyber defense strategy for your business.
You can also use paid sources like WebsitePulse and SiteLock. These tools can send notifications at the very instance of malicious activity on your site.

5. Fortify Your WordPress Security
WordPress is the most popular CMS used by 38% of websites worldwide. However, it is also the biggest target for cyber attackers. WP plugins account for 57% of these vulnerabilities.
If you are using WordPress, always check plugins and themes you use if they are stable and come from secure sources. Use strong passwords and continually update WordPress core, plugins, and themes to prevent unwanted malicious activity through your website.
6. Use the Best Malware-Scanning Tools
Use a file-based malware scanner to free your website immediately from malicious material. The scanner scans your server’s website code for viruses or unwanted PHP or HTML files.
You may use website checkers such as Web Inspector and Sucuri Sitecheck to avoid blacklisting your site due to malicious content or coding, which seriously hurts your SEO rating.
Open-source tools that have in-built web analytics reporting and system scanning. You can also use software such as Majestic or Ahrefs to search your backlink profile closely to track superfluous backlinks from SEO spammers.
7. Get an SSL Certificate for Your Website
“Secure Sockets Layer,” the SSL certificate, is a technology that encrypts connections between browsers and web servers, protects sites from cyber hackers and secures data, makes them safe and encrypted between transfers.
HTTPS guards the communication between browser and server from being intercepted and tampered with by attackers.
When 82% of audiences avoid unsecured sites, do not risk the potential loss of traffic and conversions just because you did not secure your site with an SSL certificate. Installing an SSL certificate (Secure Socket Layer certificate) on your website turns it from an HTTP to an HTTPS site.
Your SSL certificate gives you the green padlock icon, which signals audiences your website is safe for browsing and data transmission. It serves as a virtual padlock that secures all the links between the browser and the webserver. It prevents hackers from encrypting or decrypting your data.
8. Local Network Security
Manage your local network security well since you use it to access and work on your websites. Optimize several layers of device and cyber protection. Also, make sure your system and software are always updated. Update yourself as well on how to boost website security to keep your site in top shape.
Use complex passwords with two-step authentication for your website. Choose options like restricting login attempts in a fixed period, stopping idle sessions automatically, and not using virtual forms to auto-fill.
Do not forget to use data encryption through a secure Virtual Private Network (VPN) and using a Web Application Firewall (WAF). These web security measures keep your site traffic clean and safe as data is transmitted between apps, avoiding any data breach attempt.
Conclusion: Web Security Amps Your SEO
Web attacks have a long-lasting, broad-based impact on individuals and corporate networks. Web security should be a top priority for anyone using the internet. Practicing the right preventive steps must be a staple, even for SEO teams. Implement cybersecurity as part of the SEO strategy for your company to take your website’s SEO to the next level.
Mayleen Meñez used to work in media before finding her true passion in NGO work, traveling the Philippines and Asia doing so. She homeschools 3 kids and loves reinventing Filipino dishes. She is a resident SEO writer for Softvire Australia and Softvire New Zealand.

